SafetyNet Explained: Why SafetyNet Shows That Google Actually Cares About Android Root
Put yourself in Google's shoes: You know that business is becoming increasingly mobile, but the mobile operating system you maintain is wide open by design, and it's garnered legions of loyal fans that love to explore and exploit every aspect of it. There's a clear conflict of interest developing.If you maintain status quo, you'll lose valuable enterprise customers, banking apps will flee, and media companies with DRM-protected content will shun your OS. But if you lock everything down tight, you'll take away one of the main reasons many people choose your operating system over your top competitor's offering.Quite the quandary, right? Well, Google came up with a perfect compromise in the form of a system called SafetyNet, and while it's pacified one side of the argument, users who like to root and modify Android are in an uproar. The apprehension is understandable, but it's missing the point.Don't Miss: The 4 Best Phones for Privacy & Security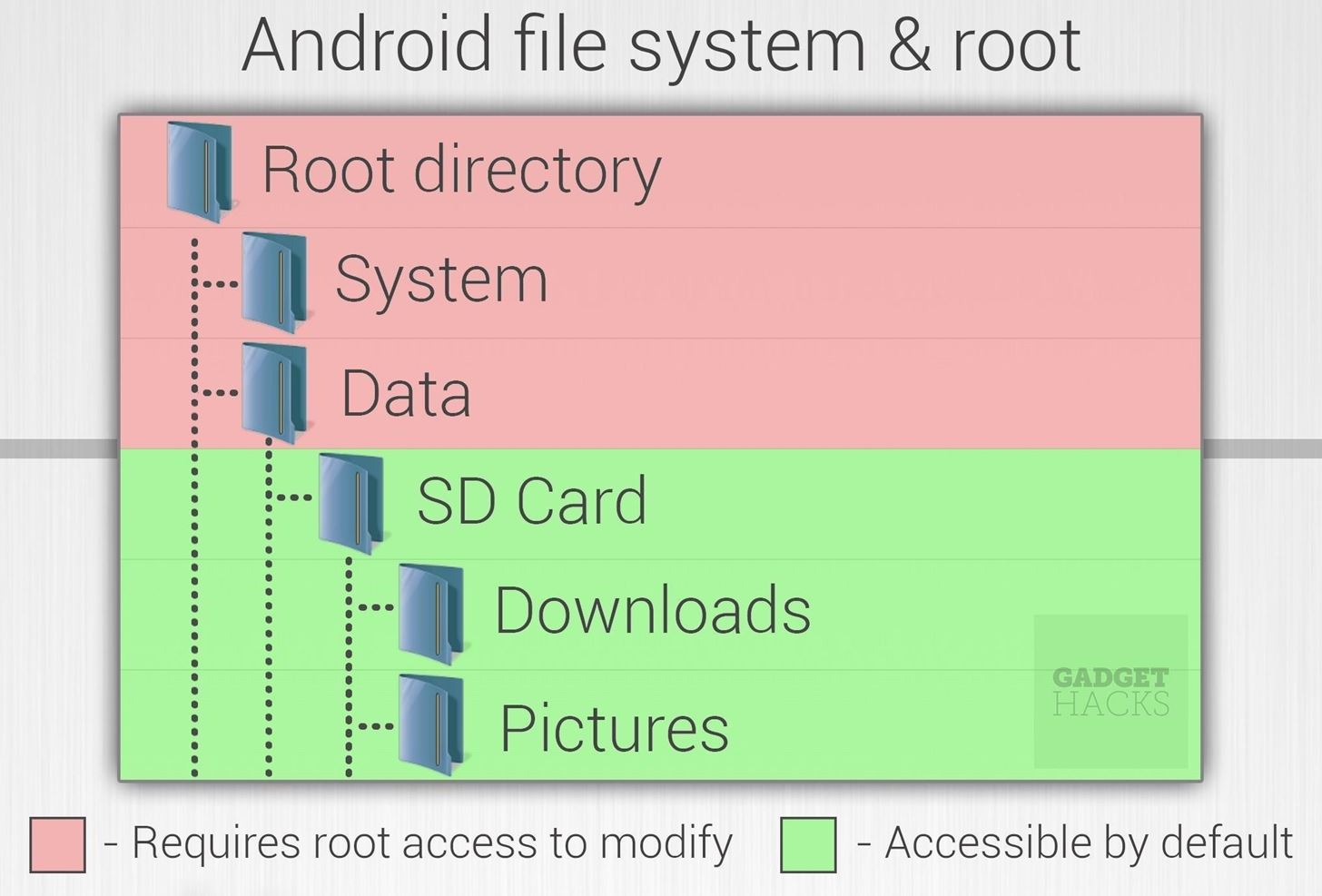
Why SafetyNet Is Good for Enterprise, Banking & DRM AppsBack in 2014, Google was facing a crisis: Many companies simply felt Android was not secure enough to allow their employees to bring Android-powered devices onto their private networks. Apps that the employee installed, as well as personal data that was stored on the device, were not fully separated from apps and proprietary data that the company may have needed to install on the device.Around this same time, Google had just added support for multiple users to Android. You'd think that would have solved the problem by allowing employers to install their apps and proprietary data to a secondary user space, but unfortunately, there was still some potential for the primary user apps to access this data. To remedy this, Google partnered with Samsung to bring some of the Korean company's KNOX security features to Android.This Android-KNOX partnership added two key features: First, user spaces were now encrypted using separate keys, and second, Android now had a system that ensured there was no interruption or hackery when booting to a user space. The second feature became known as Android Verified Boot (AVB), and it laid the groundwork for the system we now call SafetyNet. A simplified visual explanation of root. SafetyNet can tell if you've used root access to modify any files in the red-shaded area. SafetyNet expanded on many of these principles by providing an API that apps could use to see if the AVB process had been bypassed, if the device had been tampered with in any way, or if the device was not certified by Google. Put simply, if there was any funny business happening with your phone, SafetyNet could inform apps of the issue, then security-minded apps could simply refuse to run.This is where SafetyNet intersects with root. Rooted users have access to their device's entire file system, which means they could potentially copy proprietary files. But SafetyNet knows that the device is rooted in almost all cases, and it can report this fact to security-minded apps. So not only does SafetyNet pacify the enterprise segment by ensuring that proprietary data is fully sandboxed, but it also makes banking apps and DRM-protected content providers feel a lot more secure when making their services available on Android.If a company like Netflix is worried about rooted users bypassing their DRM to save pirated copies of their shows and movies, the Netflix app can just check with SafetyNet to see if the user is rooted, and if they are, simply refuse to install or run. Similarly, if a company like Chase is skeptical about getting on board with Android Pay, they can now rest assured that SafetyNet will have their backs.Don't Miss: The 5 Best Phones for Rooting & Modding
Why SafetyNet Is Good for Rooters & ModdersEverything we've talked about so far sounds like a great deal for enterprise, banking, and DRM apps — but what about those of us who mainly choose Android over iOS because of the customization options root provides? On the surface, it definitely seems like we're getting shafted since we can no longer access several apps, but if you dig a bit deeper, you'll realize this whole SafetyNet approach actually shows that Google genuinely cares about us.Most root methods utilize Fastboot to flash or boot a custom recovery image, which then allows you to install root binaries on your phone. This isn't exploiting some security loophole, either — Fastboot is actually provided by Google for the explicit purpose of flashing or booting from image files. Even when Google made some changes that would've otherwise broken Fastboot flashing, they made sure to go back and add an option to Android's Settings menu that outright allows you to enable these features by simply ticking a box (OEM unlocking). Yes, it's really this simple to enable Fastboot flashing (and thus, root) on Android. So when it comes to SafetyNet's API that lets apps know if your firmware is modified, Google had a much easier option that they declined to exercise: Just remove Fastboot and the OEM unlocking setting. If they had done that, we would've only had kernel exploits to turn to if we wanted to root — in other words, rooting would have to take place within Android instead of Fastboot or recovery mode.This would have put us in a similar position to jailbreakers on iOS lately, in that root methods would get shut down just as quickly as they popped up. In the same way that Apple doesn't have a system similar to SafetyNet, Google would have never needed to create SafetyNet if they had gone this route, as it would have been safe for enterprise, DRM, and banking apps to assume that Android users weren't rooted.Yet, Google indeed spent countless man-hours and millions of dollars creating SafetyNet — why? Because they understand that root is important to many of their users, and they wanted to give us an option: Either keep your device stock and maintain the ability to use apps that rely on SafetyNet, or go ahead and root, but know that you'll lose access to some apps.Google has since gone on to apply more restrictions to SafetyNet — most recently, they're now allowing app developers to hide their apps on the Play Store if your device fails SafetyNet's attestation check. While this may give you a feeling that they're tightening the screws, know that they're doing it for a good reason: To keep app makers happy without taking away our ability to root.Oh, and by the way — because we still have access to Fastboot flashing and custom recovery images, Android's development community has already found a way to bypass SafetyNet while being rooted. Check it out at the following link, and make sure to share your thoughts on SafetyNet in the comment section below.Don't Miss: Make Netflix & Android Pay Work on Your Rooted Device with MagiskFollow Gadget Hacks on Facebook, Twitter, Google+, and YouTube Follow Android Hacks on Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest Follow WonderHowTo on Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, and Google+
Cover image and screenshots by Dallas Thomas/Gadget Hacks
How To: Root a Nexus Device Running Android 6.0 Marshmallow How To: Update Your Nexus Without Losing Root (No Computer Needed) SafetyNet Explained: Why SafetyNet Shows That Google Actually Cares About Android Root Android Basics: A Series of Tutorials for Beginners
SafetyNet Archives - LineageOS
Yet, Google indeed spent countless man-hours and millions of dollars creating SafetyNet — why? Because they understand that root is important to many of their users, and they wanted to give us an option: Either keep your device stock and maintain the ability to use apps that rely on SafetyNet or go ahead and root, but know that you'll lose
Less than 1% of popular Android apps tested use the Google
SafetyNet Explained: Why SafetyNet Shows That Google Actually
When present, the advice parameter provides information to help explain why the SafetyNet Attestation API set either ctsProfileMatch or basicIntegrity to false in a particular result. The parameter's value contains a list of strings, such as the ones in the following example:
Google Security Engineer Explains Issues With Root and
Google Security Engineer Explains Issues With Root and Android Pay in the XDA Forums. A forum member that has been confirmed as working as a Security Engineer for Google out of Mountain View, has
Because of Android's new SafetyNet system, certain apps can now block rooted users or prevent you from accessing them altogether — but at least for now, there are still ways around these restrictions. You can pass most of SafetyNet's checks with Magisk and systemless root, but Google's Compatibility Test Suite (CTS) remains a hurdle in some
Root Exploit: Memodipper Gets You Root Access to Systems
Less than 1% of popular Android apps tested use the Google SafetyNet Attestation API Google SafetyNet helps Android developers add a layer of security to their apps to protect their apps and users from a number of potential security threats including rooted/modified devices, known malicious URLs, malware, and malicious traffic.
SafetyNet: What it is, and how it affects you on Lineage Os
Yet, Google indeed spent countless man-hours and millions of dollars creating SafetyNet — why? Because they understand that root is important to many of their users, and they wanted to give us an option: Either keep your device stock and maintain the ability to use apps that rely on SafetyNet, or go ahead and root, but know that you'll lose
Newest SafetyNet check detects System-less root (Android Pay
Yes, it's really this simple to enable Fastboot flashing (and thus, root) on Android. So when it comes to SafetyNet's API that lets apps know if your firmware is modified, Google had a much easier option that they declined to exercise: Just remove Fastboot and the OEM unlocking setting.
Magisk 101: How to Fix SafetyNet 'CTS Profile Mismatch
LOL. You have absolutely no idea what you are talking about. Keep on riding your high horse. This is about Verified Boot, not SafetyNet. There is a hash-tree based signature added to the end of the xxx.img. Reading the various images, chain of trust is established and that is how you get those new screens saying it can't trust the images, etc.
SafetyNet Attestation API | Android Developers
SafetyNet Explained: Why SafetyNet Shows That Google Actually Cares About Android Root How To: Root a Nexus 4 or Nexus 5 in Under a Minute How To: Get Root Access on OS X Mavericks and Yosemite How To: Root Any Galaxy Note 2 Variant in No Time with One Easy Click
Rooting an Alcatel Android « Null Byte :: WonderHowTo
0 comments:
Post a Comment